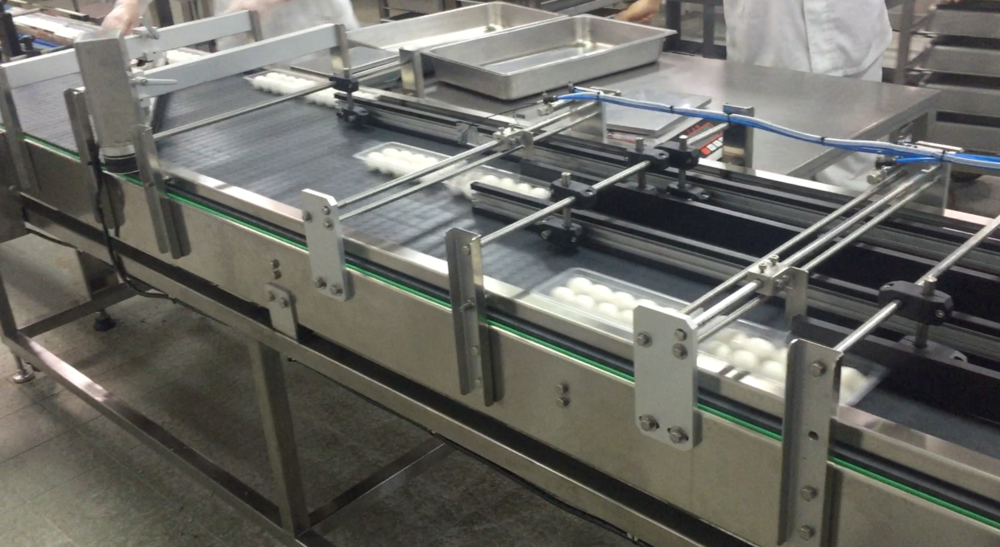
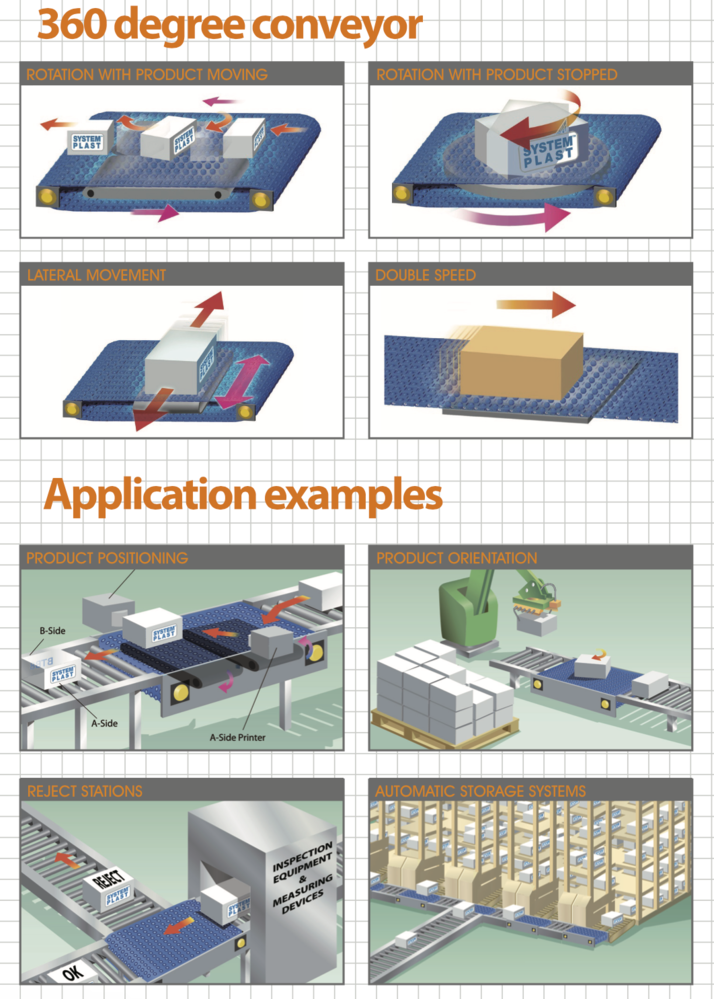
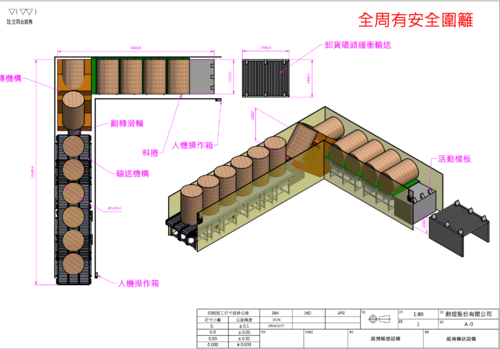
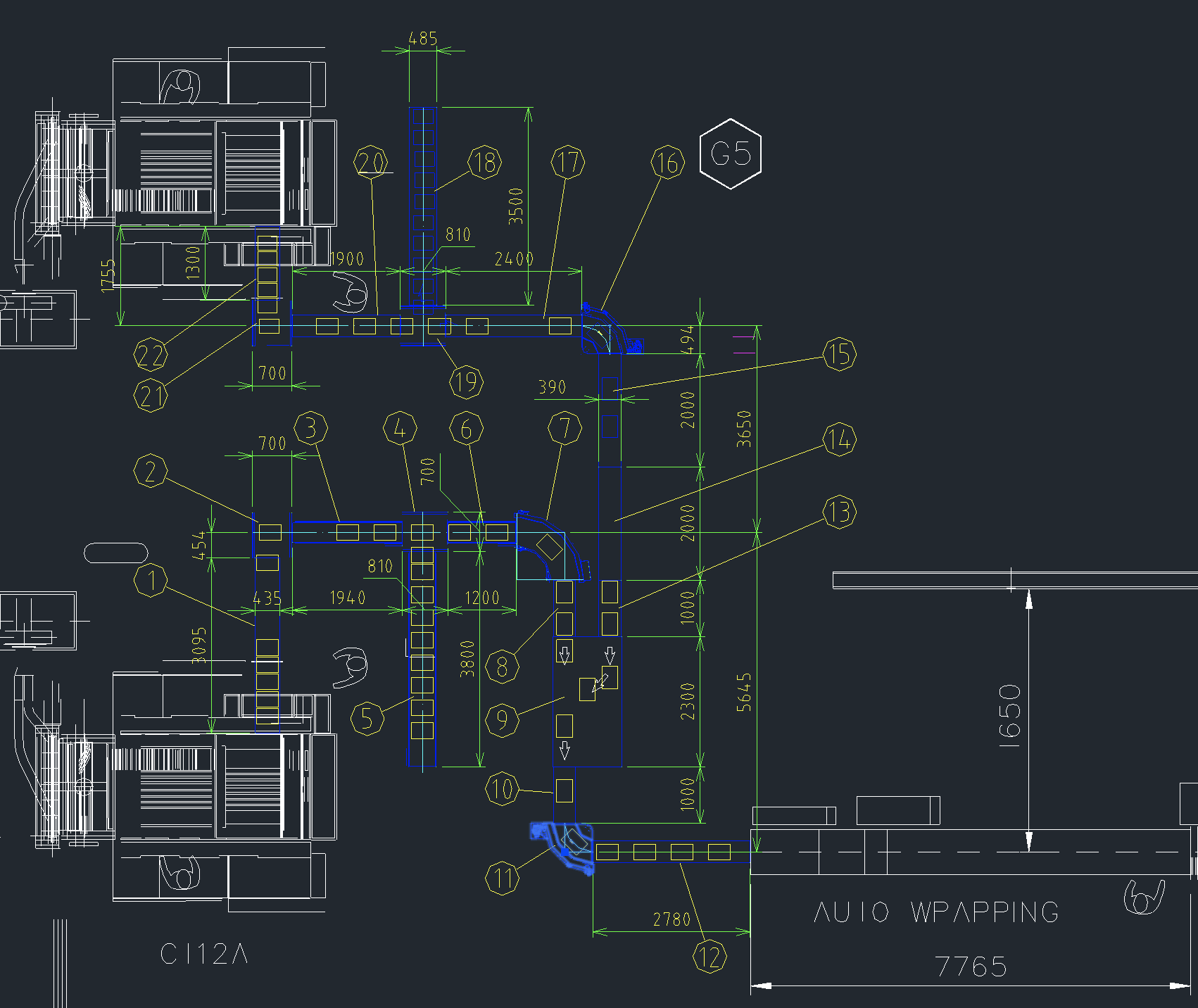
Conveyor Engineering System
Design and Planning
- Analyzing the requirements of the facility and understanding the material handling needs.
- Designing conveyor systems that are efficient, cost-effective, and meet safety standards.
- Planning the layout and integration of conveyor systems within existing or new facilities.
Material Selection
- Choosing appropriate materials for conveyor belts, rollers, and other components based on the type of materials being transported and environmental factors.
System Integration
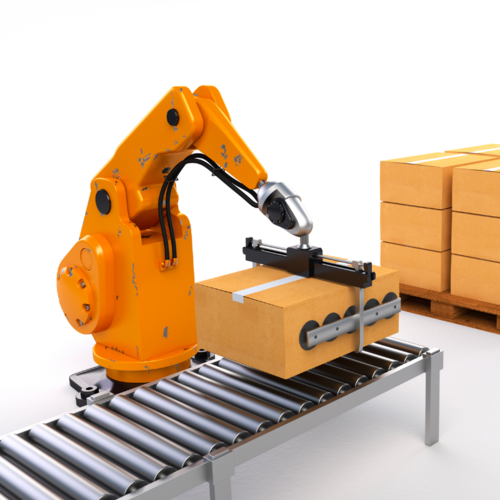
- Integrating conveyor systems with other material handling equipment and systems, such as robotic systems, sorting systems, and packaging equipment.
Automation and Control
- Implementing automation and control systems to optimize the performance of conveyor systems.
- Programming and configuring control systems for smooth and reliable operation.
Safety Compliance
- Ensuring that conveyor systems comply with safety regulations and standards.
- Implementing safety features and emergency shutdown systems.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Developing maintenance plans to ensure the longevity and reliability of conveyor systems.
- Diagnosing and troubleshooting issues with conveyor systems and implementing corrective measures.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting
- Providing cost estimates for conveyor system projects.
- Managing budgets and resources effectively.
Project Management
- Overseeing the implementation of conveyor systems from conception to completion.
- Coordinating with various stakeholders, including other engineers, project managers, and clients.
Continuous Improvement
- Evaluating the performance of existing conveyor systems and identifying opportunities for improvement.
- Staying informed about new technologies and trends in material handling and conveyor systems.
Documentation
- Creating documentation, including specifications, manuals, and training materials for end-users and maintenance teams.
Conveyor Belts
- Conveyor belts are the primary components that carry and transport materials. They come in various materials, including rubber, fabric, and metal, and can be customized based on the type of material being transported.
Rollers and Pulleys
- Rollers and pulleys provide support and guidance to conveyor belts. They are strategically placed along the conveyor system to facilitate smooth movement.
Drive Mechanism
- The drive mechanism powers the conveyor system and moves the conveyor belt. This can include electric motors, gearboxes, and other power transmission components.
Control System
- Conveyor systems often include a control system to manage the start, stop, and speed of the conveyor belt. This can be a simple manual control or a more sophisticated automated control system.
Sensors
- Sensors are used to detect the presence of materials on the conveyor belt. They play a crucial role in automation, helping control the flow of materials and preventing congestion or collisions.
Load and Unload Stations
- These are points along the conveyor system where materials are loaded onto or unloaded from the conveyor. They may include manual or automated stations depending on the application.
Sortation Systems
- In certain applications, conveyor systems are equipped with sortation mechanisms that divert materials to different lanes or chutes based on predetermined criteria.
Safety Features
- Conveyor systems are equipped with various safety features, including emergency stop buttons, guards, and sensors to ensure the safety of operators and prevent accidents.
Adjustability and Flexibility
- Many conveyor systems are designed to be adjustable and flexible to accommodate changes in production requirements. This may include adjustable height, speed, and incline/decline features.
Modularity
- Modular conveyor systems are composed of standardized components that can be easily configured and reconfigured. This allows for flexibility in system layout and expansion.
Material Selection
- The choice of materials for conveyor components (belts, rollers, etc.) is critical and depends on factors such as the type of materials being transported, environmental conditions, and the required durability.
Energy Efficiency
- Modern conveyor systems often incorporate energy-efficient components and technologies to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Maintenance Accessibility
- Conveyor systems are designed to allow easy access for maintenance and repair activities. This includes features like removable guards and easy-to-replace components.
Capacity and Throughput
- Conveyor systems are designed to handle specific capacities and throughputs. The system's design must align with the production requirements of the facility.
Noise Reduction
- Some conveyor systems incorporate features to reduce noise levels, especially in environments where noise is a concern.
Dust and Contaminant Control
- In certain industries, conveyor systems include features to control dust and prevent contamination of materials during transport.
Manufacturing and Production
- Conveyor systems are extensively used in manufacturing plants to transport raw materials, components, and finished products between different stages of the production process.
Distribution and Warehousing
- In distribution centers and warehouses, conveyor systems are employed to facilitate the movement of goods from receiving areas to storage locations and then to packing and shipping areas.
Automotive Industry
- Conveyor systems play a crucial role in the automotive industry for the assembly of vehicles. They transport car components along the assembly line, ensuring a smooth and efficient manufacturing process.
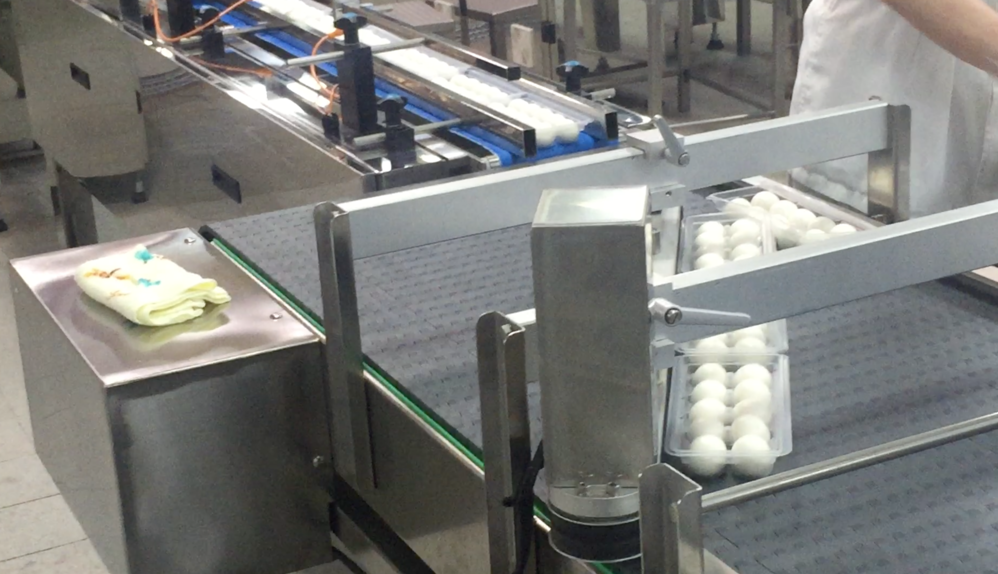
Food and Beverage Industry
- Conveyor systems are widely used in the food and beverage industry for handling and processing food products. They facilitate the movement of ingredients, packaging materials, and finished products.
Mining and Quarrying
- In mining operations, conveyor systems are used to transport bulk materials such as coal, ore, and aggregates. They help streamline the transportation of materials from extraction points to processing areas.
Retail
- In retail environments, conveyor systems assist in the movement of goods within stores, distribution centers, and during the checkout process. They are used for stocking shelves and transporting items to the point of sale.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- Conveyor systems are utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing for the handling and packaging of medications. They ensure the efficient movement of products through different processing stages.
E-commerce and Fulfillment Centers
- With the rise of online shopping, conveyor systems have become integral in e-commerce fulfillment centers. They help automate order fulfillment processes, moving products from storage to packing and shipping areas.
Recycling Facilities
- Conveyor systems are employed in recycling facilities to transport and sort recyclable materials. They assist in the efficient separation and processing of various types of recyclables.
Textile Industry
- In textile manufacturing, conveyor systems are used to transport fabrics and garments between different stages of production, including cutting, sewing, and finishing.